List Lean Round Beef Low Potassium
You may be thinking, why would Plant-Powered Kidneys talk about low potassium meats for the renal diet? Well, because some people do need or choose to include meat in their diets. And we're here to help with safe, smart, and evidence-based information.
In this article, we'll be talking about low potassium meats and situations where they may fit into a renal diet.
Meat and Protein in the Renal Diet
While we will be discussing low potassium meats in this article, it's also important to understand a bit about protein and meat in general.
How much protein should I have with kidney disease?
Depending on the stage and cause of kidney damage, protein and animal meats may be encouraged or limited.
In the early stages of CKD (stages 1-3), there is research to show that high protein diets should be avoided. In other words, limiting protein may or may not be helpful depending on your current protein intake. If you're not eating an excessive amount of protein you may not need to reduce your protein intake.
However, for late stages of CKD (stages 4-5 not on dialysis), a low protein diet is recommended in most cases to preserve kidney function.
Learn more about a low protein diet here.
Is animal protein okay for the renal diet?
Depending on your stage and situation, animal protein may or may not be okay. Therefore, it's important to discuss with your own dietitian and nephrologist about your diet needs.
If you have kidney disease and are working to change your diet to avoid dialysis, limiting animal protein has been shown to delay CKD progression.
However, there are situations in which including low potassium meats may be acceptable.
When could low potassium meats be helpful?
While a lot of research has proven that a plant-based diet is beneficial for kidney disease, there can be certain situations in which a fully plant-based diet is not necessary or recommended.
Dialysis
Dialysis is a life-sustaining treatment to replace kidney function. This starts when a person has end-stage kidney disease (otherwise considered stage 5 kidney disease) and is not feeling well.
The process of dialysis includes cleaning the blood by hemodialysis or pulling wastes through the abdomen in peritoneal dialysis.
Either process also includes the removal of some protein. That protein needs to be replaced in the diet. In many cases, protein supplements are recommended to provide a person with enough protein.
Learn more about protein supplements on dialysis here.
Cultural and Religious Preferences
There are certain dietary preferences that include cultural and religious beliefs. As registered dietitians, we always want to honor personal preferences.
In these cases, we may recommend low potassium meats to help maintain potassium balance when needed.
When would low potassium meats be bad?
There are some situations where meats, even low potassium meats, may not be helpful.
Stage 4 or Stage 5 Renal Diet
If you are following a special diet for stage 4 or stage 5 kidney disease, you may need to reduce your protein intake.
If you're working on cutting back on the protein in your diet, it may be helpful to stick to the low potassium meats as you work on making changes.
Read our guide for stage 4 kidney disease here.
Read our guide for stage 5 kidney disease here.
A Low Potassium Diet Restriction
If you have been directed to follow a low potassium diet, it's important to consider that meats will also provide potassium.
Many people immediately look to cut back on tomatoes, bananas, avocados, and other potassium-rich fruits and vegetables. However, there's also a risk of not getting enough nutrients when eliminating these kinds of foods.
Read more about the low potassium diet here.
High Phosphorus Levels
For someone with high phosphorus levels in their renal function panel or other lab results, limiting animal meats – even low potassium meats – can be incredibly helpful to lower phosphorus levels.
Animal proteins have a higher absorption rate of phosphorus than plant proteins. Read more about the low phosphorus diet here.
Defining Low Potassium Food
We need to start by defining what makes certain foods, including meat, low in potassium.
A food that is low in potassium has less than 200 milligrams of potassium per serving.
The standard serving size of meat is 3 ounces. This will be approximately the size of a deck of standard playing cards.
Many foods are analyzed in 100-gram serving sizes. This helps standardize the comparisons between different meats that can be different portions.
A 100-gram amount of cooked meat is approximately 3.5 ounces of cooked meat.
Potassium in Chicken, Red Meats and Game Meats
There are not a lot of low potassium meat options in chicken, turkey, and other common meats.
The lowest in this category is chicken wings, which is 206 milligrams per 100-gram serving (about 3.5 ounces). One chicken wing is approximately 1 ounce. The 100-gram serving is approximately 3-4 chicken wings.
A chicken drumstick is approximately 104 grams and has 239 milligrams of potassium in 100 grams. As discussed, this is not considered a low potassium food.
Chicken and turkey are generally lower in potassium when compared to beef, lamb, and pork. However, these animal meats are not considered low potassium meats as they are above the 200-milligram threshold.
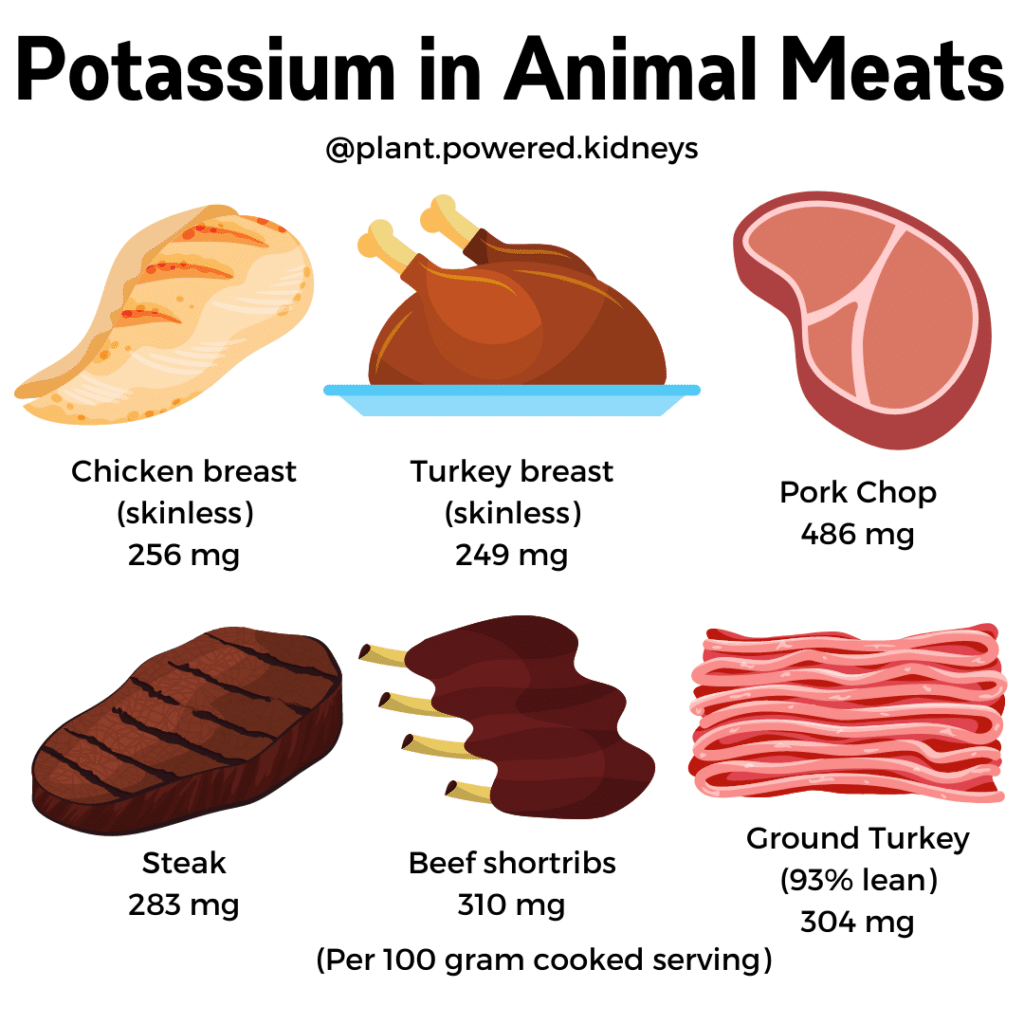
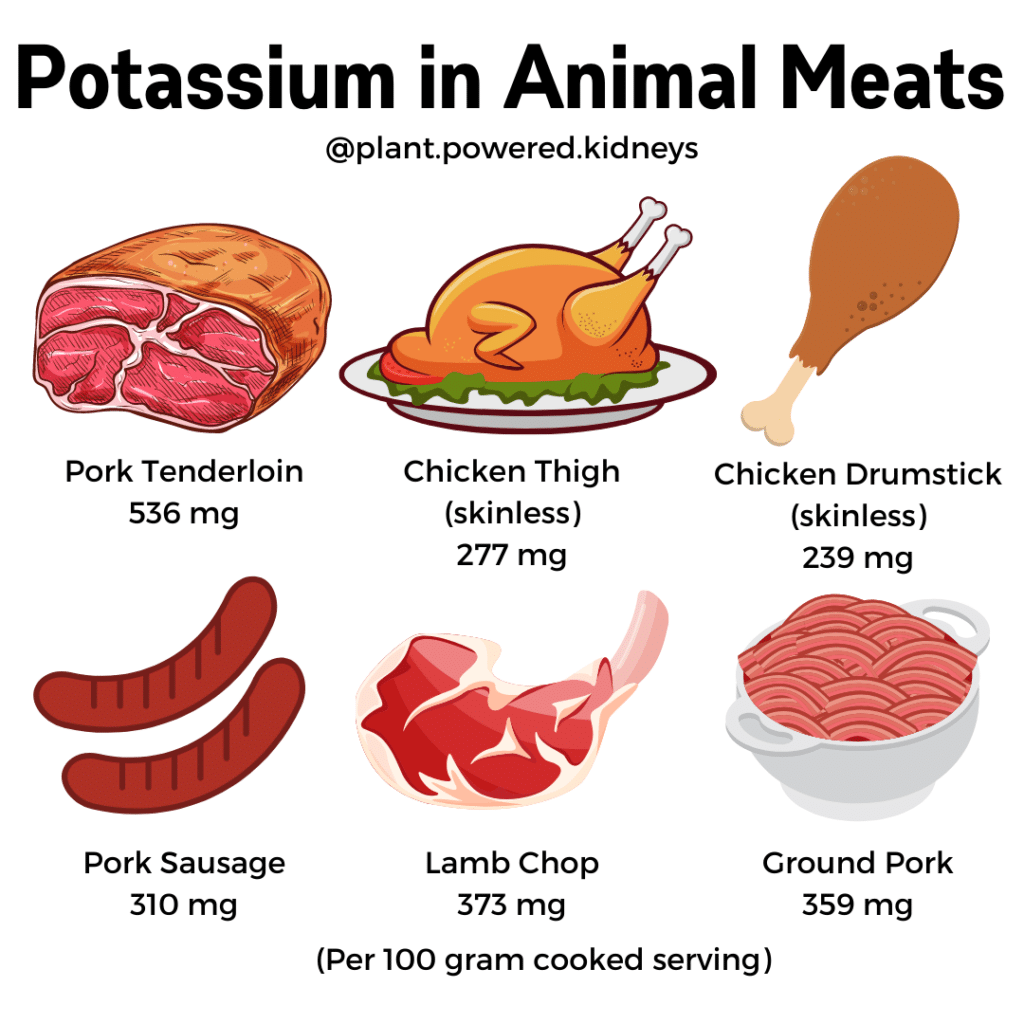
Chart of Potassium in Meats, Fish, and Deli
Below is a chart of a variety of meats and their potassium content per 100-milligram cooked or ready-to-eat serving.
| Meat | Potassium (mg) in 100g serving |
|---|---|
| Chicken breast (skinless) | 256 |
| Chicken thigh (skinless) | 277 |
| Chicken drumstick (skinless) | 239 |
| Chicken wing | 206 |
| Ground Chicken | 292 |
| Duck (skinless) | 251 |
| Turkey breast (skinless) | 249 |
| Ground Turkey (93% lean) | 304 |
| Ground Beef | 302 |
| Steak | 283 |
| Beef Shortribs | 310 |
| Pork Chop | 486 |
| Pork Tenderloin | 536 |
| Pork Ribs | 317 |
| Pork Sausage | 310 |
| Ground Pork | 359 |
| Lamb Chop | 373 |
| Venison | 311 |
| Beef liver | 349 |
| Sweetbreads | 431 |
Potassium in Fish and Seafood
Most fish and seafood are also considered high in potassium. However, unlike chicken and other common meats, there are some more low potassium meats available in this category.
Clams have just 58 milligrams of potassium per 100-gram serving.
A 100-gram (3.5 ounces) serving of shrimp has 101 milligrams of potassium, making it one of the low potassium meats.
Canned light tuna has 176 milligrams of potassium per 100-gram serving. It's important to know that many canned tunas have added phosphorus, so be sure to read the labels to avoid unhealthy additives.
Oysters have 193 milligrams of potassium per serving. This also qualifies as low potassium.
Chart of Potassium in Fish and Seafood
Below is a chart showing the potassium content of various fish and shellfish.
| Fish or Shellfish | Potassium (mg) in 100g serving |
|---|---|
| Abalone | 448 |
| Anchovy | 544 |
| Carp | 356 |
| Catfish | 382 |
| Clams | 58 |
| Cod | 297 |
| Crab | 319 |
| Crayfish | 294 |
| Eel | 291 |
| Flounder | 203 |
| Haddock | 362 |
| Halibut | 549 |
| Herring | 413 |
| Lobster | 247 |
| Mackerel | 436 |
| Mussels | 573 |
| Ocean Perch | 200 |
| Octopus | 626 |
| Oysters | 193 |
| Perch | 340 |
| Pike | 328 |
| Salmon | 391 |
| Sea Bass | 324 |
| Scallops | 253 |
| Shrimp | 101 |
| Squid | 441 |
| Swordfish | 528 |
| Tilapia | 382 |
| Trout | 476 |
| Tuna (canned, light) | 176 |
| Tuna (fresh) | 557 |
The nutrition information above was filtered by baked, broiled, or steamed cooking methods.
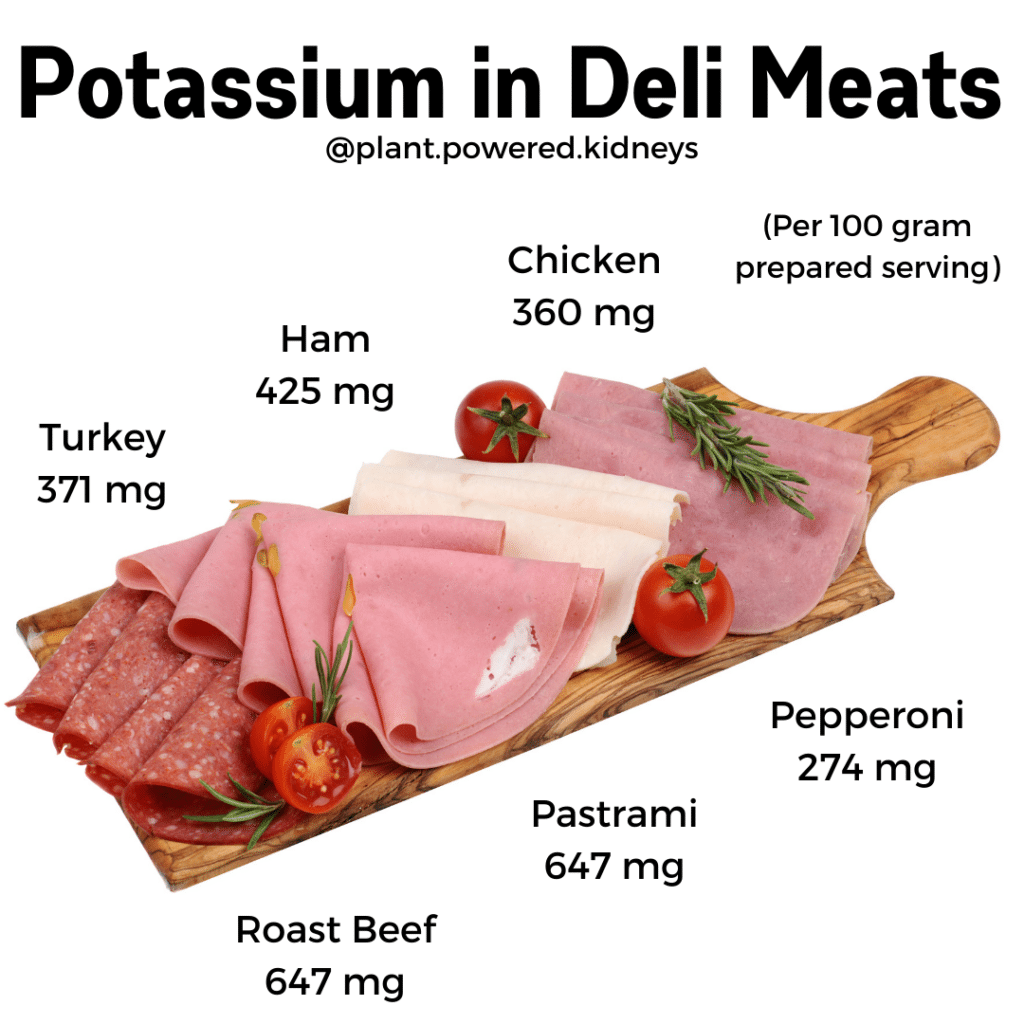
Potassium in Deli Meats
Deli meats are not often recommended for the renal diet. This is because they are quite often high in nutrients that need to be limited like sodium, potassium, and phosphorus.
| Deli & Processed Meats | Potassium (mg) in 100g serving |
|---|---|
| Turkey (deli slices) | 371 |
| Ham (deli slices) | 425 |
| Turkey-Ham (deli slices) | 299 |
| Chicken (deli slices) | 360 |
| Roast Beef (deli slices) | 647 |
| Bologna | 147 |
| Pastrami | 647 |
| Salami | 363 |
| Corned Beef | 136 |
| Bacon | 557 |
| Turkey Bacon | 666 |
| Canadian Bacon | 999 |
| Liverwurst | 199 |
| Pepperoni | 274 |
| Hot Dog (beef) | 343 |
| Bratwurst | 348 |
| Kielbasa | 306 |
Deli Meats in the Renal Diet
An important note about deli meats, even low potassium meats, is to beware of sodium and additives. These are important to limit and avoid when possible.
Deli meats also come in a variety of low-sodium meat options as well. This may not always be a wise choice.
A study published in 2022 found that the low-sodium deli meats had an average of 44% more potassium than the original deli meats.
One specific deli meat in the study had 1,500 milligrams of potassium in exchange for 25% less sodium.
Instead of deli meats, try making tuna salad, chicken salad, or chickpea salad. Even a peanut butter and jelly sandwich can be a better option for a renal diet!
Does heat destroy potassium in foods?
Many people wonder about cooking their meats to help lower the potassium content.
It is true that cooking can lower the amount of potassium in certain foods. This has been studied with potatoes, beans, and some other foods.
It has also been studied with meat.
Boiling, Pressure Cooking, and Microwaving Meats
While boiling has been shown to drastically lower potassium content in potatoes, it has also been shown to lower potassium levels in meat.
Boiling meats for at least 10 minutes has been shown to reduce potassium content by about half.
In one study, beef liver, beef strips, hamburger, and salmon were assessed after periods of cooking. After up to 8 hours of cooking in water, potassium content was reduced in each by over 92%.
Hot dogs, ham, and canned tuna were also tested. Hot dogs had the least amount of potassium removed, resulting in a 43% reduction.
That being said, more research is needed to determine how much potassium can be consistently removed by the different cooking methods.
Does leaching meats lower the potassium content?
Leaching, or soaking in water, has been traditionally recommended to lower the potassium content of foods. This has been primarily studied with potatoes and certain types of vegetables.
However, research has shown that leaching is not an effective way to lower potassium content of certain foods as compared to double-boiling or even normal boiling.
Potassium Additives in Meat
Another concern about meat is the potassium additives. More and more research and questions are popping up about the impact of potassium additives in the renal diet.
This is particularly important to those on a potassium restriction.
Some common potassium additives include;
- Potassium nitrate
- Potassium chloride
- Tetrapotassium phosphate
- Potassium sorbate
- Potassium tripolyphosphate
However, some of these above are also considered phosphorus additives. This is another thing to beware of on the renal diet.
Learn more about phosphate additives here.
Potassium chloride is the main salt substitution in many salt-free substitutes. This is why salt substitutes are not recommended – they are extremely high in potassium.
Summary
When we think of the low potassium diet, we don't think about low potassium meats. But as we have seen here, there are actually few meats that do qualify as being low in potassium.
If you need to restrict the potassium in your diet, it can be incredibly helpful to protect your kidneys by reducing the potassium sources of animal meats and other proteins. In short, most meats, fish, and seafood are considered high in potassium.
Some of the lowest potassium meats are clams, oysters, and tuna.
Chicken and turkey aren't considered low potassium meats, but they are lower than other types of meats.
Deli meats are not only high in potassium but can also be high in sodium and contain phosphorus additives. For these reasons, deli meats should be avoided when possible.
Which one of the meats in this article surprised you the most? Comment below with your thoughts!
Other articles you may enjoy
Source: https://www.plantpoweredkidneys.com/low-potassium-meats/
0 Response to "List Lean Round Beef Low Potassium"
Post a Comment